Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 induced by H
induced by H O
O and
and  -irradiation
-irradiationKumagai, Yuta; Fidalgo, A. B.*; Jonsson, M.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 123(15), p.9919 - 9925, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:63.7(Chemistry, Physical)Radiation-induced oxidative dissolution of uranium dioxide (UO ) is one of the most important chemical processes of U driven by redox reactions. We have examined the effect of UO
) is one of the most important chemical processes of U driven by redox reactions. We have examined the effect of UO stoichiometry on the oxidative dissolution of UO
stoichiometry on the oxidative dissolution of UO induced by hydrogen peroxide (H
induced by hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) and
) and  -ray irradiation. By comparing the reaction kinetics of H
-ray irradiation. By comparing the reaction kinetics of H O
O between stoichiometric UO
between stoichiometric UO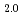 and hyper-stoichiometric UO
and hyper-stoichiometric UO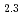 , we observed a significant difference in reaction speed and U dissolution kinetics. The stoichiometric UO
, we observed a significant difference in reaction speed and U dissolution kinetics. The stoichiometric UO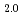 reacted with H
reacted with H O
O much faster than the hyper-stoichiometric UO
much faster than the hyper-stoichiometric UO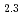 . The U dissolution from UO
. The U dissolution from UO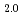 was initially much lower than that from UO
was initially much lower than that from UO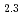 , but gradually increased as the oxidation by H
, but gradually increased as the oxidation by H O
O proceeded. The
proceeded. The  -ray irradiation induced the U dissolution that is analogous to the kinetics by the exposure to a low concentration (0.2 mM) of H
-ray irradiation induced the U dissolution that is analogous to the kinetics by the exposure to a low concentration (0.2 mM) of H O
O . The exposure to higher H
. The exposure to higher H O
O concentrations caused lower U dissolution and resulted in deviation from the U dissolution behavior by
concentrations caused lower U dissolution and resulted in deviation from the U dissolution behavior by  -ray irradiation.
-ray irradiation.
 O
O and
and  -ray induced oxidative dissolution of stoichiometric UO
-ray induced oxidative dissolution of stoichiometric UO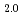
Kumagai, Yuta; Fidalgo, A. B.*; Jonsson, M.*
no journal, ,
We have investigated the effect of UO -hyper-stoichiometry on the oxidative dissolution upon H
-hyper-stoichiometry on the oxidative dissolution upon H O
O exposure and by water radiolysis. The oxidative dissolution of UO
exposure and by water radiolysis. The oxidative dissolution of UO is anticipated in the concept of geological disposal of spent nuclear fuel and also in the direct contact with coolant water after a severe accident. However, our understanding on the dissolution kinetics has so far not taken the hyper-stoichiometric nature of UO
is anticipated in the concept of geological disposal of spent nuclear fuel and also in the direct contact with coolant water after a severe accident. However, our understanding on the dissolution kinetics has so far not taken the hyper-stoichiometric nature of UO into account. Thus, we have studied the oxidative dissolution of hyper-stoichiometric UO
into account. Thus, we have studied the oxidative dissolution of hyper-stoichiometric UO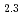 and stoichiometric UO
and stoichiometric UO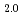 and compared the results. The results show that the UO
and compared the results. The results show that the UO stoichiometry largely affects the kinetics of oxidative dissolution. The oxidation of stoichiometric UO
stoichiometry largely affects the kinetics of oxidative dissolution. The oxidation of stoichiometric UO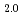 in water proceeded fast accompanied with low initial U dissolution, but gradually the reaction became slower and U dissolution became more significant.
in water proceeded fast accompanied with low initial U dissolution, but gradually the reaction became slower and U dissolution became more significant.